Adsorption of pharmaceutically active compounds - new publication

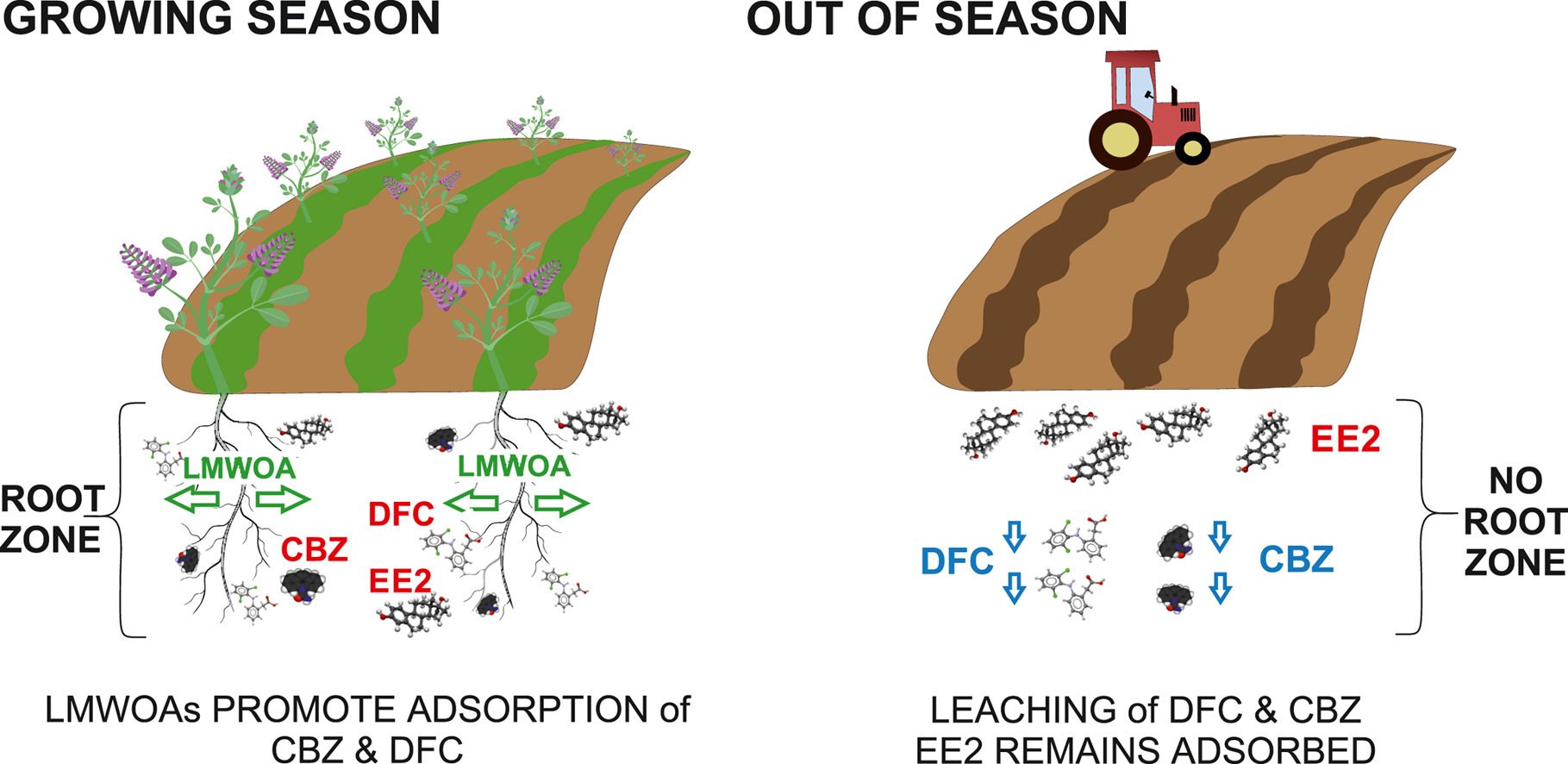
Lili Szabó and her co-authors have published a paper in Chemosphere examining the adsorption mechanisms of pharmaceutically active compounds and hormones onto soil particles via irrigation. The study finds that root acids primarily compete for adsorption sites rather than altering pH during the growing season. Consequently, hormones can leach from the topsoil into deeper layers or become bioavailable. Conversely, during winter, hormones tend to adsorb onto soil particles, with stream water, rather than irrigation water, being the primary source of these molecules.